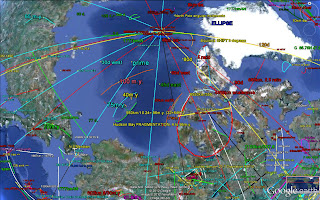
Cyclical PERIODIC variations of the POLES (Milankovich
relations) or N-S crustal block LINEARS are well-known:
1. POLAR WOBBLE at a constant tilt angle
has a 41 (40.96) k.y. PERIOD, completing a 360 degree ROTATION with a regular
FLAT and LEVEL inscription (SHEAR) on the Earth’s CRUST;
2. POLAR TILT ANGLE cycles regularly
(gradually) each 25,000 years- changing the Latitude of the Tropics of Cancer and
Capricorn;
3. POSITION of the Earth, relative to
the EARTH-SUN average SEPARATION (spacing), cycles each 100,000 years (102.4
k.y.?).
I have found additional CYCLICAL CHANGES, which do not negate Milankovitch’s
findings, but AUGMENT THEM:
A. TIME PASSAGE allows VERTICAL to
offset LATERAL GRAVITATIONAL SHIFT, creating UPLIFT (or SINKING) of
ELLIPTICALLY-EXHIBITED “JERKS”, chatter, and POLYGONS (a CUBIC EQUATION);
B. The combination of above movements
occurs on many SCALES- from shearing of a SMALL OUTCROP to that of a
CONTINENTAL LAND MASS;
MULTIPLYING the SCALE by one million:
C. The LENGTH of SHEAR LINES (linears)
occurs 2 different ways:
I. MULTIPLES of 2, by the BINARY THEOREM, e.g.
32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096 km, m, or mm. These are DIVISIBLE by
1.6- the Venus RATIO. This is in CONFLICT with:
II. MULTIPLES of 500,
e.g. 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, up to 40Kkm- the EARTH CIRCUMFERENCE. These are
DIVISIBLE by 2.5- the Jupiter RATIO (an ALGEBRAIC EQUATION).
D. MULTIPLES (HARMONICS) occur at 1000
and 100 x SCALES: 40.96 m.y.- the TIMED COMPLETION of a POLAR TILT CYCLE, and
at 4.096 b.y.- the AGE of LUNAR GRAVITATIONAL LATERAL MOVEMENT INITIATION. CONFLICT Creates HEAT, LATERAL SHIFT
(thrust Faulting), and SHEAR- all VIOLENT on the LARGER SCALES.
E. EROSION is LATERAL GRAVITATIONALLY-INDUCED,
as higher-in elevation MOUNDS are “twisted” and HARDENED in the process.
Metamorphism is initiated whenever the rotation-COMPRESSION reduces the ROCK POROSITY to
zero. The direction of rotation may be found from the position of “PINCHING OUT”
of the resulting TERRACES.
Above SAND MOUNTAIN UPLIFT consists of a CRUSTAL BLOCK- which is subdivided into smaller SINKS and RISES:
The RISE- which is a TILTED PARTIAL CIRCLE- is on a TIME SCALE MULTIPLE of Milankovitch's 41 k.y. AXIAL CYCLE:
ADJACENT CW and CCW-ROTATING blocks have slightly different rotation rates, so that the SHEAR loosens the Jn Jurassic Navajo sandstone; this is done in a CIRCULAR ARC path, allowing the WINTER North wind to move it back to the south, and to shift it again in summer with the SSW wind (notice the 135 degrees change of the wind direction- 3/8th of a circle- creating an atmospheric OCTAGON!):
The FULCRUM, or center of rotation, lies in the CENTERLINE BETWEEN the 2 rotating arcs. It is not filled with the OMNI-PRESENT LOOSE SAND, even though precipitation regularly flows through this BOTTOM-of-the-CHANNEL. The water evidently flows down, to emerge in the NOW COVERED Santa Fe springs, under lake Sand Hollow:
This EQUATION is a trigonometric one, with a
SINUSOIDAL VARIATION; and,
F. SMALL SCALE DYNAMICS create conflict
on a SMALL SCALE, e.g. warm-hot springs, pentagon to octagon shift in OUTCROPS,
and STRATA TILTING.
The "BOILER) is a 77F warm spring, and the site of the NEXT 20.48 km SEPARATION VOLCANO (from Hf, and twice that distance from CRATER HILL VOLCANO):
Pah Tempe Hot Springs(108F) occurs at the JUNCTION of the Hurricane Fault and the Virgin River:
Warm Springs (77F) State Park, NV exhibits a RISE moving northward into a SINK, inside an ANALEMMA (partial figure 8):
The "TWIST" is EXHIBITED at EROSIONAL REMNANTS, where the HARDENED SANDSTONE resists erosion more than un-twisted outcrops. This results in TERRACES- narrowing in the TWIST DIRECTION (CCW for RISES):
These are for CHECKERBOARD MESA- an EROSIONAL REMNANT at Zion NP, UT:
Sand Hollow REMNANTS show similar EROSIONAL FEATURES:
Above are on SMALL SCALES, and they also occur on LARGE SCALES- such as for TERRACES, commonly named CONTINENTAL SHELVES:
The VARIOUS EQUATIONS I leave for your PUZZLE SOLUTIONS; they DO NOT REQUIRE a higher degree in MATHEMATICS. When I get some ATTEMPTS, I will release them to the GENERAL PUBLIC!
Here is a STARTER:
EROSION = K, constant x height
difference (sine {tilt angle}), so that erosion is maximum for a vertical CONE, and zero at
a zero slope. The tilt angle is found by measuring the angular uplift of a
rising hill or MOUND, and this depends upon the VERTICAL UPLIFT RATE x time.
Gravitational attraction of the BLOCK operates in a WAVE-LIKE fashion, and this
raises the mound relative to the ground surface. The mounds do NOT RISE
relative to their base, since they appear to be STRATIGRAPHICALLY CONSISTENT at
the few adjacent remnants visible. The Mounds rise via EROSION of the base
surrounding them, and they remain un-eroded due to “TWISTING” COMPACTION. They
are HARDENED as their porosity decreases, becoming METAMORPHOSED after pore
space becomes zero, e.g. sandstone going to quartzite with
compression-compaction. Gravitational rising cannot be measured in man’s
lifetime, so that TWISTING must be measured instead. I have been cataloguing these
BLOCK ROTATIONAL RATES, and they are near 1 degree/time unit, regardless of the
year, k.y. or m.y. time interval. These relate to the size of the block, e.g.
years for a meter-size outcrop, k.y. for a km block, or m.y. for a Kkm-sized
block. For this portion of the EROSION EQUATION:
EROSION= K sine
{angular rotation RATE (TIME)} = zero, for zero time and rate, and MAXIMUM for
large rates or times. The pertinent rotation rate may be found by measuring the
angular change between ADJACENT LINEARS within a TRAPEZOIDAL BLOCK of crust,
and this is part of the ANALYSIS of the TIME INTERVAL, LINEAR DIVIDER of the
block, and measurement of the POLYGON surrounding the block. There remains the
COMPACTION-COMPRESSION component resistance to erosion, and this is a
trigonometric relation also:
EROSION= K
sine {angular rate (time)} x [1 – K'cosine (slope angle)] so that it is zero for
zero slope angle (flat), and maximum for vertical slopes. The constant K' must be different than K, so that it must be solved independantly.
SLOPE ANGLE may be measured directly in the field. Usually slope is less than the angle of repose (near 30-45 degrees), but may be almost vertical for cases such as Zion NP, UT where the AGE is less than 2 m.y. (and twist-compaction hardening is maximized).The constant K must be consistent with the desired EROSION RATE, such as mm/year. RATES will be near 1 mm/year or less, and this offsets continental EXPANSION- which is a NET 1 mm/year, for 4096 km ORB for E-W North America, South America, and Australia since the LATERAL TIDAL GRAVITATIONAL INITIATION at 4.096 billion years.
SLOPE ANGLE may be measured directly in the field. Usually slope is less than the angle of repose (near 30-45 degrees), but may be almost vertical for cases such as Zion NP, UT where the AGE is less than 2 m.y. (and twist-compaction hardening is maximized).The constant K must be consistent with the desired EROSION RATE, such as mm/year. RATES will be near 1 mm/year or less, and this offsets continental EXPANSION- which is a NET 1 mm/year, for 4096 km ORB for E-W North America, South America, and Australia since the LATERAL TIDAL GRAVITATIONAL INITIATION at 4.096 billion years.